Objective-C Runtime 特性2:Method Swizzling
学习runtime机制不得不理解Method Swizzling。Method Swizzling是改变一个selector的实际实现的技术。通过这一技术,我们可以在运行时通过修改类的分发表中selector对应的函数,来修改方法的实现。
实现 Method Swizzling
一个常见的例子就是在开发中我们需要跟踪程序中每一个view controller展示给用户的次数:当然,我们可以在每个view controller的viewDidAppear中添加跟踪代码;但是这太过麻烦,需要在每个view controller中写重复的代码。创建一个子类可能是一种实现方式,但需要同时创建UIViewController, UITableViewController, UINavigationController及其它UIKit中view controller的子类,这同样会产生许多重复的代码。
这种情况下,我们就可以使用Method Swizzling,如在代码所示:
#import <objc/runtime.h>
@implementation UIViewController (Tracking)
// Invoked whenever a class or category is added to the Objective-C runtime
+ (void)load
{
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
Class class = [self class];
// When swizzling a class method, use the following:
// Class class = object_getClass((id)self);
// the method might not exist in the class, but in its superclass
SEL originalSelector = @selector(viewWillAppear:);
SEL swizzledSelector = @selector(xxx_viewWillAppear:);
Method originalMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(class, originalSelector);
Method swizzledMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(class, swizzledSelector);
// class_addMethod will fail if original method already exists
BOOL didAddMethod = class_addMethod(class,
originalSelector,
method_getImplementation(swizzledMethod),
method_getTypeEncoding(swizzledMethod));
// the method doesn’t exist and we just added one
if (didAddMethod) {
class_replaceMethod(class,
swizzledSelector,
method_getImplementation(originalMethod),
method_getTypeEncoding(originalMethod));
}
else {
method_exchangeImplementations(originalMethod, swizzledMethod);
}
});
}
#pragma mark - Method Swizzling
- (void)xxx_viewWillAppear:(BOOL)animated
{
[self xxx_viewWillAppear:animated];
NSLog(@"viewWillAppear: %@", self);
}
// 看上去是会导致无限循环的。但并不会出现这种情况。在swizzling的过程中,方法中的[self xxx_viewWillAppear:animated]已经被重新指定到UIViewController类的-viewWillAppear:中。不过如果我们调用的是[self viewWillAppear:animated],则会产生无限循环,因为这个方法的实现在运行时已经被重新指定为xxx_viewWillAppear:了。
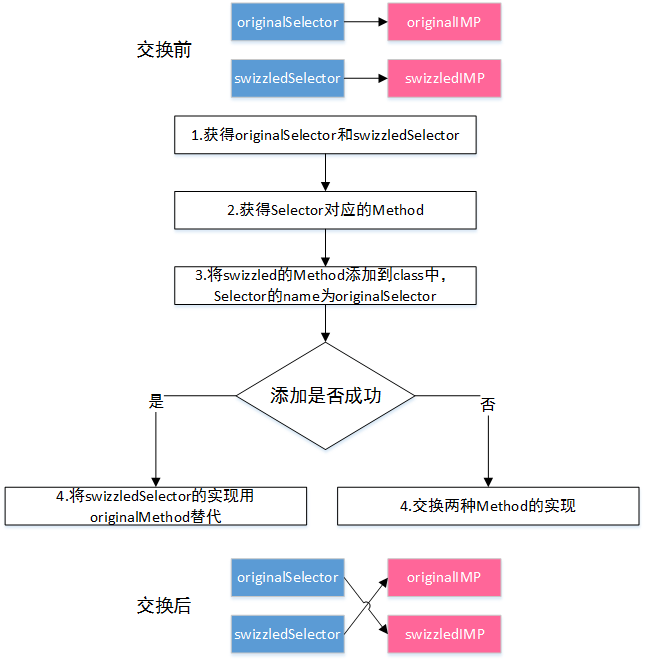
说明:
-
第3步中如果 originalMethod 已经存在,则添加失败。
-
失败则直接交换 originalMethod 和 swizzledMethod;若成功,则说明该类本身没有实现 originalMethod,第2步中
Method originalMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(class, originalSelector);获取都是父类的 originalMethod,这时候 originalSelector 已指向 swizzledMethod,我们需要的就是将 swizzledSelector 指向父类的 originalMethod。
Swizzling应该总是在+load中执行
在Objective-C中,运行时会自动调用每个类的两个方法。+load会在类初始加载时调用,+initialize会在第一次调用类的类方法或实例方法之前被调用。这两个方法是可选的,且只有在实现了它们时才会被调用。由于method swizzling会影响到类的全局状态,因此要尽量避免在并发处理中出现竞争的情况。+load能保证在类的初始化过程中被加载,并保证这种改变应用级别的行为的一致性。相比之下,+initialize在其执行时不提供这种保证—事实上,如果在应用中没为给这个类发送消息,则它可能永远不会被调用。
理解 选择器、方法与实现
在Objective-C中,选择器(selector)、方法(method)和实现(implementation)是运行时中一个特殊点,虽然在一般情况下,这些术语更多的是用在消息发送的过程描述中。
以下是Objective-C Runtime Reference中的对这几个术语一些描述:
- Selector(typedef struct objc_selector *SEL):用于在运行时中表示一个方法的名称。一个方法选择器是一个C字符串,它是在Objective-C运行时被注册的。选择器由编译器生成,并且在类被加载时由运行时自动做映射操作。
- Method(typedef struct objc_method *Method):在类定义中表示方法的类型
- Implementation(typedef id (*IMP)(id, SEL, …)):这是一个指针类型,指向方法实现函数的开始位置。每一个参数是指向对象自身的指针(self),第二个参数是方法选择器。然后是方法的实际参数。
typedef struct objc_method *Method;
struct objc_method {
SEL method_name OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; // 方法名
char *method_types OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
IMP method_imp OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; // 方法实现
}
理解这几个术语之间的关系最好的方式是:一个类维护一个运行时可接收的消息分发表`objc_method_list;分发表中的每个入口是一个方法(Method),其中key是一个特定名称,即选择器(SEL),其对应一个实现(IMP),即指向底层C函数的指针。
Aspect Oriented Programming (面向切面编程)
An aspect can alter the behavior of the base code by applying advice (additional behavior) at various join points (points in a program) specified in a quantification or query called a pointcut (that detects whether a given join point matches).
在 Objective-C 中,这句话意思就是利用 Runtime 特性给指定的方法添加自定义代码。有很多方式可以实现 AOP ,Method Swizzling 就是其中之一。而且幸运的是,目前已经有一些第三方库可以让你不需要了解 Runtime ,就能直接开始使用 AOP 。
Aspects 就是一个不错的 AOP 库,封装了 Runtime , Method Swizzling 这些黑色技巧,只提供两个简单的API:
/// Adds a block of code before/instead/after the current `selector` for a specific class.
///
/// @param block Aspects replicates the type signature of the method being hooked.
/// The first parameter will be `id<AspectInfo>`, followed by all parameters of the method.
/// These parameters are optional and will be filled to match the block signature.
/// You can even use an empty block, or one that simple gets `id<AspectInfo>`.
///
/// @note Hooking static methods is not supported.
/// @return A token which allows to later deregister the aspect.
+ (id<AspectToken>)aspect_hookSelector:(SEL)selector
withOptions:(AspectOptions)options
usingBlock:(id)block
error:(NSError **)error;
/// Adds a block of code before/instead/after the current `selector` for a specific instance.
- (id<AspectToken>)aspect_hookSelector:(SEL)selector
withOptions:(AspectOptions)options
usingBlock:(id)block
error:(NSError **)error;
/// Deregister an aspect.
/// @return YES if deregistration is successful, otherwise NO.
id<AspectToken> aspect = ...;
[aspect remove];