iOS Core Animation
寄宿图(CALayer的内容)
contents:图片(CGImageRef,它是一个指向CGImage结构的指针。)layer.contents = (__bridge id)image.CGImage;contentsGravity:图片显示模式(与UIView的contentMode属性对应)layer.contentsGravity = kCAGravityResizeAspect;contentsScale:定义寄宿图的像素尺寸和视图大小的比例,默认1.0将会以每个点1个像素绘制图片,如果设置为2.0,则会以每个点2个像素绘制图片(适配 Retina)layer.contentsScale = [UIScreen mainScreen].scale;masksToBounds:是否显示超出边界的内容layer.masksToBounds = YES;contentsRect:寄宿图的显示区域(矩形),使用单位坐标,默认(0,0,1,1)layer.contentsRect = CGRectMake(0, 0, 0.5, 0.5);contentsCenter:是一个CGRect,它定义了一个固定的边框和一个在图层上可拉伸的区域,矩形内的内容在水平和垂直两个方向拉伸,类似于UIImage的resizableImageWithCapInsets:`layer.contentsCenter = CGRectMake(0.25, 0.25, 0.5, 0.5)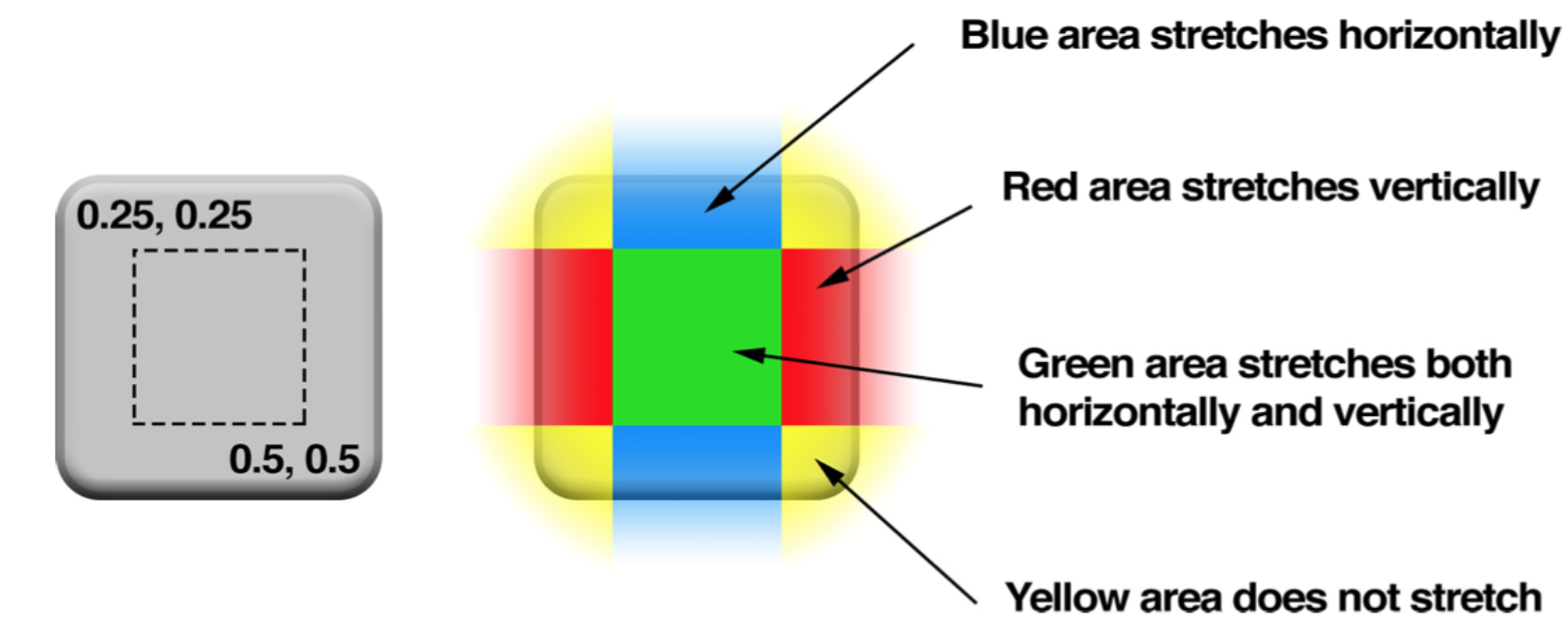
图层几何学
- UIView的布局属性:frame,bounds和center,对应CALayer的frame,bounds和position。
anchorPoint:图层的锚点,可以认为anchorPoint是用来移动图层的把柄,用单位坐标来描述,当改变了anchorPoint,position属性保持固定的值不变,但是frame却移动了。layer.anchorPoint = CGPointMake(0.5f, 0.9f);CALayer在不同坐标系间的转换
- (CGPoint)convertPoint:(CGPoint)point fromLayer:(CALayer *)layer;
- (CGPoint)convertPoint:(CGPoint)point toLayer:(CALayer *)layer;
- (CGRect)convertRect:(CGRect)rect fromLayer:(CALayer *)layer;
- (CGRect)convertRect:(CGRect)rect toLayer:(CALayer *)layer;
- Z坐标轴:
zPosition、anchorPointZ - Hit Testing:
-containsPoint:【需要将坐标转成每个图层坐标系下的坐标】、-hitTest:【CALayer *layer = [self.layerView.layer hitTest:point];】
视觉效果
- 圆角:
layer.cornerRadius = 20.0f; - 图层边框和颜色:
layer.borderWidth = 5.0f;layer.borderColor = [UIColor greenColor].CGColor; - 阴影:
shadowOpacity【在0.0(不可见)和1.0(完全不透明)之间的浮点数】、shadowColor、shadowOffset【控制阴影的方向和距离,是一个CGSize的值,宽度控制这阴影横向的位移,高度控制着纵向的位移】、shadowRadius【控制阴影的模糊度,当它的值是0的时候,阴影就和视图一样有一个非常确定的边界线。当值越来越大的时候,边界线看上去就会越来越模糊和自然】 - 阴影裁剪:阴影通常就是在Layer的边界之外,如果你开启了masksToBounds属性,所有从图层中突出来的内容都会被才剪掉。如果想沿着内容裁切,需要用到两个图层:一个只画阴影的空的外图层【在外图层中添加阴影效果】,和一个用
masksToBounds裁剪内容的内图层【内图层中使用裁剪】。 shadowPath:实时计算阴影也是一个非常消耗资源的,尤其是图层有多个子图层。shadowPath是一个CGPathRef类型(一个指向CGPath的指针)layer.shadowPath = squarePath;mask图层蒙板:mask本身就是个CALayer类型,类似于一个子图层,相对于父图层(即拥有该属性的图层)布局,定义了父图层的部分可见区域【mask相当于一个镂空的物体去截取父图层】- 拉伸过滤:
minificationFilter【缩小】、magnificationFilter【放大】{kCAFilterLinear(默认)、kCAFilterNearest、kCAFilterTrilinear} - 组透明:
shouldRasterize实现组透明的效果,如果它被设置为YES,在应用透明度之前,图层及其子图层都会被整合成一个整体的图片。为了启用shouldRasterize属性,要设置图层的rasterizationScale属性。默认情况下,所有图层拉伸都是1.0, 所以如果使用了shouldRasterize属性,就要确保设置了rasterizationScale属性去匹配屏幕,以防止出现Retina屏幕像素化的问题。layer.shouldRasterize = YES; layer.rasterizationScale = [UIScreen mainScreen].scale;
变换
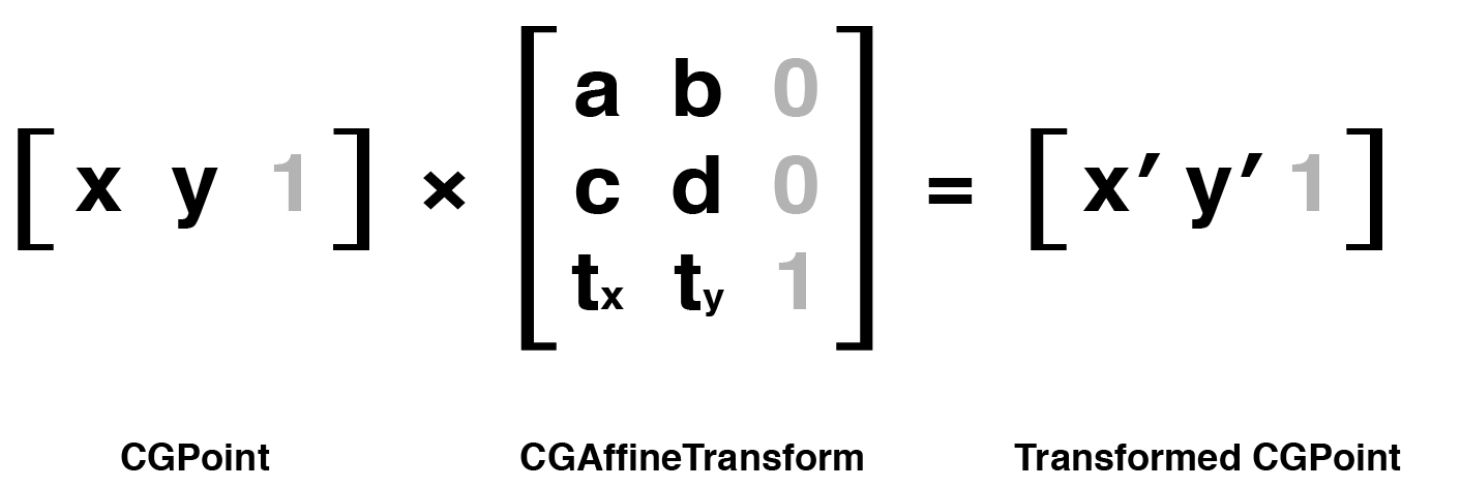
仿射变换(CGAffineTransform)【平移、旋转、缩放、斜切】
UIView可以通过设置transform属性做变换,但实际上它只是封装了内部图层的变换。CALayer同样也有一个transform属性,但它的类型是CATransform3D,而不是CGAffineTransform,CALayer对应于UIView的transform属性叫做affineTransform。
CGAffineTransformMakeRotation(CGFloat angle)
CGAffineTransformMakeScale(CGFloat sx, CGFloat sy)
CGAffineTransformMakeTranslation(CGFloat tx, CGFloat ty)
- 混合变换:在一个变换的基础上做更深层次的变换
CGAffineTransformRotate(CGAffineTransform t, CGFloat angle)
CGAffineTransformScale(CGAffineTransform t, CGFloat sx, CGFloat sy)
CGAffineTransformTranslate(CGAffineTransform t, CGFloat tx, CGFloat ty)
CGAffineTransformIdentity//单位矩阵
CGAffineTransformConcat(CGAffineTransform t1, CGAffineTransform t2);//在两个变换的基础上创建一个新的变换
- 斜切变换:不常用
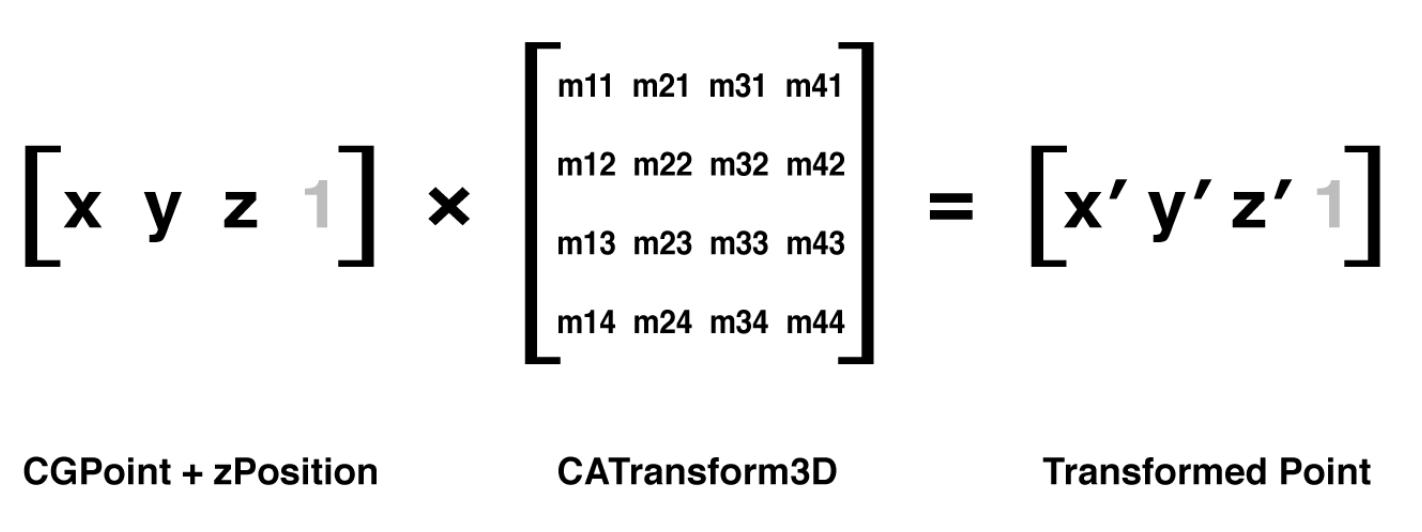
3D 变换
CATransform3DMakeRotation(CGFloat angle, CGFloat x, CGFloat y, CGFloat z)
CATransform3DMakeScale(CGFloat sx, CGFloat sy, CGFloat sz)
CATransform3DMakeTranslation(Gloat tx, CGFloat ty, CGFloat tz)
- 透视投影:
CATransform3D的透视效果通过矩阵中一个很简单的元素来控制:m34。m34用于按比例缩放X和Y的值来计算到底要离视角多远。m34的默认值是0,我们可以通过设置m34为-1.0 / d来应用透视效果,d代表了想象中视角相机和屏幕之间的距离,以像素为单位,那应该如何计算这个距离呢?实际上并不需要,大概估算一个就好了。因为视角相机实际上并不存在,所以可以根据屏幕上的显示效果自由决定它的放置的位置。通常500-1000就已经很好了,但对于特定的图层有时候更小或者更大的值会看起来更舒服,减少距离的值会增强透视效果,所以一个非常微小的值会让它看起来更加失真,然而一个非常大的值会让它基本失去透视效果。 - 灭点:当在透视角度绘图的时候,远离相机视角的物体将会变小变远,当远离到一个极限距离,它们可能就缩成了一个点,于是所有的物体最后都汇聚消失在同一个点。做3D变换的时候要时刻记住这一点,当视图通过调整m34来让它更加有3D效果,应该首先把它放置于屏幕中央,然后通过平移来把它移动到指定位置(而不是直接改变它的position),这样所有的3D图层都共享一个灭点。
sublayerTransform属性:是CATransform3D类型,它影响到所有的子图层。这意味着可以一次性对包含这些图层的容器做变换,于是所有的子图层都自动继承了这个变换方法。可以通过设置父视图的透视变换,可以保证子视图有相同的透视和灭点。- 背面:图层是双面绘制的,反面显示的是正面的一个镜像图片。
doubleSided的属性来控制图层的背面是否要被绘制
专用图层
CAShapeLayer
CAShapeLayer是一个通过矢量图形来绘制的图层子类。可以指定诸如颜色和线宽等属性,用CGPath来定义想要绘制的图形,最后CAShapeLayer就自动渲染出来。
//create shape layer
CAShapeLayer *shapeLayer = [CAShapeLayer layer];
shapeLayer.strokeColor = [UIColor redColor].CGColor;
shapeLayer.fillColor = [UIColor clearColor].CGColor;
shapeLayer.lineWidth = 5;
shapeLayer.lineJoin = kCALineJoinRound;
shapeLayer.lineCap = kCALineCapRound;
shapeLayer.path = path.CGPath;
//add it to our view
[self.containerView.layer addSublayer:shapeLayer];
- 圆角(UIBezierPath有自动绘制圆角矩形的构造方法,可以单独指定矩形的每个角)
//define path parameters
CGRect rect = CGRectMake(50, 50, 100, 100);
CGSize radii = CGSizeMake(20, 20);
UIRectCorner corners = UIRectCornerTopRight | UIRectCornerBottomRight | UIRectCornerBottomLeft;
//create path
UIBezierPath *path = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithRoundedRect:rect byRoundingCorners:corners cornerRadii:radii];
CATextLayer
Core Animation提供了一个CALayer的子类CATextLayer,它以图层的形式包含了UILabel几乎所有的绘制特性,并且额外提供了一些新的特性。
//create a text layer
CATextLayer *textLayer = [CATextLayer layer];
textLayer.frame = self.labelView.bounds;
textLayer.contentsScale = [UIScreen mainScreen].scale;// 适配 Retina
[self.labelView.layer addSublayer:textLayer];
//set text attributes
textLayer.foregroundColor = [UIColor blackColor].CGColor;
textLayer.alignmentMode = kCAAlignmentJustified;
textLayer.wrapped = YES;
//choose a font
UIFont *font = [UIFont systemFontOfSize:15];
//set layer font
CFStringRef fontName = (__bridge CFStringRef)font.fontName;
CGFontRef fontRef = CGFontCreateWithFontName(fontName);
textLayer.font = fontRef;
textLayer.fontSize = font.pointSize;
CGFontRelease(fontRef);
//choose some text
NSString *text = @"Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing \ elit. Quisque massa arcu, eleifend vel varius in, facilisis pulvinar \ leo. Nunc quis nunc at mauris pharetra condimentum ut ac neque. Nunc elementum, libero ut porttitor dictum, diam odio congue lacus, vel \ fringilla sapien diam at purus. Etiam suscipit pretium nunc sit amet \ lobortis";
//set layer text
textLayer.string = text;
CATransformLayer
CAGradientLayer
CAGradientLayer是用来生成两种或更多颜色平滑渐变的。用Core Graphics复制一个CAGradientLayer并将内容绘制到一个普通图层的寄宿图也是有可能的,但是CAGradientLayer的真正好处在于绘制使用了硬件加速。
//create gradient layer and add it to our container view
CAGradientLayer *gradientLayer = [CAGradientLayer layer];
gradientLayer.frame = self.containerView.bounds;
[self.containerView.layer addSublayer:gradientLayer];
//set gradient colors
gradientLayer.colors = @[(__bridge id)[UIColor redColor].CGColor, (__bridge id)[UIColor blueColor].CGColor];
//set gradient start and end points
gradientLayer.startPoint = CGPointMake(0, 0);
gradientLayer.endPoint = CGPointMake(1, 1);
colors属性可以包含很多颜色。默认情况下,这些颜色在空间上均匀地被渲染,但是可以用locations属性来调整空间。locations属性是一个浮点数值的数组(以NSNumber包装)。这些浮点数定义了colors属性中每个不同颜色的位置,同样的,也是以单位坐标系进行标定。0.0代表着渐变的开始,1.0代表着结束。
locations数组并不是强制要求的,但是如果给它赋值了就一定要确保locations的数组大小和colors数组大小一定要相同,否则你将会得到一个空白的渐变。
//set gradient colors
gradientLayer.colors = @[(__bridge id)[UIColor redColor].CGColor, (__bridge id) [UIColor yellowColor].CGColor, (__bridge id)[UIColor greenColor].CGColor];
//set locations
gradientLayer.locations = @[@0.0, @0.25, @0.5];
CAReplicatorLayer
CAScrollLayer
CAScrollLayer有一个-scrollToPoint:方法,它自动适应bounds的原点以便图层内容出现在滑动的地方。注意,这就是它做的所有事情。前面提到过,Core Animation并不处理用户输入,所以CAScrollLayer并不负责将触摸事件转换为滑动事件,既不渲染滚动条,也不实现任何iOS指定行为例如滑动反弹。
//get the offset by subtracting the pan gesture
//translation from the current bounds origin
CGPoint offset = self.bounds.origin;
offset.x -= [recognizer translationInView:self].x;
offset.y -= [recognizer translationInView:self].y;
//scroll the layer
[(CAScrollLayer *)self.layer scrollToPoint:offset];
//reset the pan gesture translation
[recognizer setTranslation:CGPointZero inView:self];
CATiledLayer
CAEmitterLayer
是一个高性能的粒子引擎,被用来创建实时例子动画如:烟雾,火,雨等等这些效果。
CAEAGLLayer
AVPlayerLayer
是由AVFoundation提供的,它和Core Animation紧密地结合在一起,提供了一个CALayer子类来显示自定义的内容类型。
AVPlayerLayer是用来在iOS上播放视频的。是高级接口例如MPMoivePlayer的底层实现,提供了显示视频的底层控制。AVPlayerLayer的使用相当简单:可以用+playerLayerWithPlayer:方法创建一个已经绑定了视频播放器的图层,或者可以先创建一个图层,然后用player属性绑定一个AVPlayer实例。
//get video URL
NSURL *URL = [[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@"Ship" withExtension:@"mp4"];
//create player and player layer
AVPlayer *player = [AVPlayer playerWithURL:URL];
AVPlayerLayer *playerLayer = [AVPlayerLayer playerLayerWithPlayer:player];
//set player layer frame and attach it to our view
playerLayer.frame = self.containerView.bounds;
[self.containerView.layer addSublayer:playerLayer];
//play the video
[player play];
隐式动画
事务
Core Animation基于一个假设:屏幕上的任何东西都可以(或者可能)做动画。当改变CALayer的一个可做动画的属性,它并不能立刻在屏幕上体现出来。相反,它是从先前的值平滑过渡到新的值。这一切都是默认的行为,不需要做额外的操作。这其实就是所谓的隐式动画。之所以叫隐式是因为我们并没有指定任何动画的类型,动画执行的时间取决于当前事务的设置。
事务实际上是Core Animation用来包含一系列属性动画集合的机制,任何用指定事务去改变可以做动画的图层属性都不会立刻发生变化,而是当事务一旦提交的时候开始用一个动画过渡到新值。Core Animation在每个run loop周期中自动开始一次新的事务,即使你不显式的用[CATransaction begin]开始一次事务,任何在一次run loop循环中属性的改变都会被集中起来,然后做一次0.25秒的动画。
事务是通过CATransaction类来做管理,CATransaction没有属性或者实例方法,并且也不能用+alloc和-init方法创建它。但是可以用+begin和+commit分别来入栈或者出栈。任何可以做动画的图层属性都会被添加到栈顶的事务,你可以通过+setAnimationDuration:方法设置当前事务的动画时间,或者通过+animationDuration方法来获取值(默认0.25秒)。
- (IBAction)changeColor
{
//begin a new transaction
[CATransaction begin];
//set the animation duration to 1 second
[CATransaction setAnimationDuration:1.0];
//randomize the layer background color
CGFloat red = arc4random() / (CGFloat)INT_MAX;
CGFloat green = arc4random() / (CGFloat)INT_MAX;
CGFloat blue = arc4random() / (CGFloat)INT_MAX;
self.colorLayer.backgroundColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:red green:green blue:blue alpha:1.0].CGColor;
//commit the transaction
[CATransaction commit];
}
完成块
基于UIView的block的动画允许你在动画结束的时候提供一个完成的动作。CATranscation接口提供的+setCompletionBlock:方法也有同样的功能。
//add the spin animation on completion
[CATransaction setCompletionBlock:^{
//rotate the layer 90 degrees
CGAffineTransform transform = self.colorLayer.affineTransform;
transform = CGAffineTransformRotate(transform, M_PI_2);
self.colorLayer.affineTransform = transform;
}];
action
改变属性时CALayer自动应用的动画称作action,当CALayer的属性被修改时候,它会调用-actionForKey:方法,传递属性的名称。剩下的操作都在CALayer的头文件中有详细的说明,实质上是如下几步:
- 图层首先检测它是否有委托,并且是否实现CALayerDelegate协议指定的
-actionForLayer:forKey方法。如果有,直接调用并返回结果。 - 如果没有委托,或者委托没有实现
-actionForLayer:forKey方法,图层接着检查包含属性名称对应行为映射的actions字典。 - 如果actions字典没有包含对应的属性,那么图层接着在它的style字典接着搜索属性名。
- 最后,如果在style里面也找不到对应的行为,那么图层将会直接调用定义了每个属性的标准行为的
-defaultActionForKey:方法。
所以一轮完整的搜索结束之后,-actionForKey:要么返回空(这种情况下将不会有动画发生),要么是CAAction协议对应的对象,最后CALayer拿这个结果去对先前和当前的值做动画。
UIKit是如何禁用隐式动画的:每个UIView对它关联的图层都扮演了一个委托,并且提供了-actionForLayer:forKey的实现方法。当不在一个动画块的实现中,UIView对所有图层行为返回nil,但是在动画block范围之内,它就返回了一个非空值。
当然返回nil并不是禁用隐式动画唯一的办法,CATransaction有个方法叫做+setDisableActions:,可以用来对所有属性打开或者关闭隐式动画。[CATransaction setDisableActions:YES];
呈现层
每个图层属性的显示值都被存储在一个叫做呈现图层的独立图层当中,他可以通过-presentationLayer方法来访问。这个呈现图层实际上是模型图层的复制,但是它的属性值代表了在任何指定时刻当前外观效果。
注意呈现图层仅仅当图层首次被提交(就是首次第一次在屏幕上显示)的时候创建,所以在那之前调用-presentationLayer将会返回nil。
显示动画
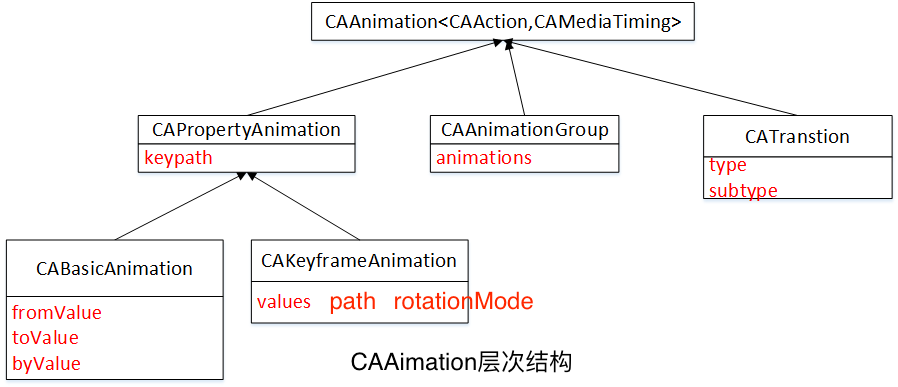
CALayer添加动画- (void)addAnimation:(CAAnimation * nonnull)anim forKey:(NSString * nullable)key
属性动画
属性动画作用于图层的某个单一属性,并指定了它的一个目标值,或者一连串将要做动画的值。属性动画分为两种:基础和关键帧。
基础动画
CABasicAnimation是CAPropertyAnimation的一个子类。CAPropertyAnimation通过指定动画的keyPath作用于一个单一属性,CAAnimation通常应用于一个指定的CALayer,于是这里指的也就是一个图层的keyPath。
CABasicAnimation继承于CAPropertyAnimation,并添加了如下属性:id fromValue、id toValue 、id byValue。
//create a basic animation
CABasicAnimation *animation = [CABasicAnimation animation];
animation.keyPath = @"backgroundColor";
animation.toValue = (__bridge id)color.CGColor;
//uncomment the two lines below to solve the snap-back problem
//没有下面两行背景会变成以前的颜色,因为动画并没有改变图层的模型,而只是呈现层
animation.fromValue = (__bridge id)self.colorLayer.backgroundColor;
self.colorLayer.backgroundColor = color.CGColor;
//apply animation to layer
[self.colorLayer addAnimation:animation forKey:nil];
CAAnimationDelegate
使用隐式动画的时候,可以在CATransaction完成块中检测到动画的完成。但是这种方式并不适用于显式动画,因为这里的动画和事务并没太多关联。为了知道一个显式动画在何时结束,需要使用一个实现了CAAnimationDelegate协议的delegate。
- (IBAction)changeColor
{
//create a new random color
CGFloat red = arc4random() / (CGFloat)INT_MAX;
CGFloat green = arc4random() / (CGFloat)INT_MAX;
CGFloat blue = arc4random() / (CGFloat)INT_MAX;
UIColor *color = [UIColor colorWithRed:red green:green blue:blue alpha:1.0];
//create a basic animation
CABasicAnimation *animation = [CABasicAnimation animation];
animation.keyPath = @"backgroundColor";
animation.toValue = (__bridge id)color.CGColor;
animation.delegate = self;
//apply animation to layer
[self.colorLayer addAnimation:animation forKey:nil];
}
//代理方法
- (void)animationDidStop:(CABasicAnimation *)anim finished:(BOOL)flag
{
//set the backgroundColor property to match animation toValue
// 设置一个新的事务,并且禁用图层行为。否则动画会发生两次,一个是因为显式的CABasicAnimation,另一次是因为隐式动画
[CATransaction begin];
[CATransaction setDisableActions:YES];
self.colorLayer.backgroundColor = (__bridge CGColorRef)anim.toValue;
[CATransaction commit];
}
关键帧动画
//create a keyframe animation
CAKeyframeAnimation *animation = [CAKeyframeAnimation animation];
animation.keyPath = @"backgroundColor";
animation.duration = 2.0;
animation.values = @[
(__bridge id)[UIColor blueColor].CGColor,
(__bridge id)[UIColor redColor].CGColor,
(__bridge id)[UIColor greenColor].CGColor,
(__bridge id)[UIColor blueColor].CGColor ];
//apply animation to layer
[self.colorLayer addAnimation:animation forKey:nil];
提供一个数组的值就可以按照颜色变化做动画,但一般来说用数组来描述动画运动并不直观。CAKeyframeAnimation有另一种方式去指定动画,就是使用CGPath。
//create the keyframe animation
CAKeyframeAnimation *animation = [CAKeyframeAnimation animation];
animation.keyPath = @"position";
animation.duration = 4.0;
animation.path = bezierPath.CGPath;
//图层将会根据曲线的切线自动旋转
animation.rotationMode = kCAAnimationRotateAuto;
[shipLayer addAnimation:animation forKey:nil];
动画组
CABasicAnimation和CAKeyframeAnimation仅仅作用于单独的属性,而CAAnimationGroup可以把这些动画组合在一起。CAAnimationGroup是另一个继承于CAAnimation的子类,它添加了一个animations数组的属性,用来组合别的动画。
//create group animation
CAAnimationGroup *groupAnimation = [CAAnimationGroup animation];
groupAnimation.animations = @[animation1, animation2];
groupAnimation.duration = 4.0;
//add the animation to the color layer
[colorLayer addAnimation:groupAnimation forKey:nil];
Transition过渡
属性动画只对图层的可动画属性起作用,所以如果要改变一个不能动画的属性(比如图片),或者从层级关系中添加或者移除图层,属性动画将不起作用。
于是就有了过渡的概念。过渡并不像属性动画那样平滑地在两个值之间做动画,而是影响到整个图层的变化。过渡动画首先展示之前的图层外观,然后通过一个交换过渡到新的外观。
为了创建一个过渡动画,我们将使用CATransition,同样是另一个CAAnimation的子类,和别的子类不同,CATransition有一个type和subtype来标识变换效果。type属性是一个NSString类型,可以被设置成如下类型:kCATransitionFade 、kCATransitionMoveIn 、kCATransitionPush 、kCATransitionReveal。
//图片切换淡入淡出效果
- (IBAction)switchImage
{
//set up crossfade transition
CATransition *transition = [CATransition animation];
transition.type = kCATransitionFade;
//apply transition to imageview backing layer
[self.imageView.layer addAnimation:transition forKey:nil];
//cycle to next image
UIImage *currentImage = self.imageView.image;
NSUInteger index = [self.images indexOfObject:currentImage];
index = (index + 1) % [self.images count];
self.imageView.image = self.images[index];
}
隐式过渡
CATransision可以对图层任何变化平滑过渡的事实使得它成为那些不好做动画的属性图层行为的理想候选。苹果当然意识到了这点,并且当设置了CALayer的content属性的时候,CATransition的确是默认的行为。但是对于视图关联的图层,或者是其他隐式动画的行为,这个特性依然是被禁用的,但是对于你自己创建的图层,这意味着对图层contents图片做的改动都会自动附上淡入淡出的动画。
图层树动画
CATransition并不作用于指定的图层属性,这就是说你可以在即使不能准确得知改变了什么的情况下对图层做动画,例如,在不知道UITableView哪一行被添加或者删除的情况下,直接就可以平滑地刷新它,或者在不知道UIViewController内部的视图层级的情况下对两个不同的实例做过渡动画。
//UITabBarController平滑过渡
- (void)tabBarController:(UITabBarController *)tabBarController didSelectViewController:(UIViewController *)viewController
{
//set up crossfade transition
CATransition *transition = [CATransition animation];
transition.type = kCATransitionFade;
//apply transition to tab bar controller's view
[self.tabBarController.view.layer addAnimation:transition forKey:nil];
}
自定义动画
做过渡动画基础的原则就是对原始的图层外观截图,然后添加一段动画,平滑过渡到图层改变之后那个截图的效果。
对图层做截图还是很简单的。CALayer有一个-renderInContext:方法,可以通过把它绘制到Core Graphics的上下文中捕获当前内容的图片,然后在另外的视图中显示出来。如果我们把这个截屏视图置于原始视图之上,就可以遮住真实视图的所有变化,于是重新创建了一个简单的过渡效果。
- (IBAction)performTransition
{
//preserve the current view snapshot
UIGraphicsBeginImageContextWithOptions(self.view.bounds.size, YES, 0.0);
[self.view.layer renderInContext:UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext()];
UIImage *coverImage = UIGraphicsGetImageFromCurrentImageContext();
//insert snapshot view in front of this one
UIView *coverView = [[UIImageView alloc] initWithImage:coverImage];
coverView.frame = self.view.bounds;
[self.view addSubview:coverView];
//update the view (we'll simply randomize the layer background color)
CGFloat red = arc4random() / (CGFloat)INT_MAX;
CGFloat green = arc4random() / (CGFloat)INT_MAX;
CGFloat blue = arc4random() / (CGFloat)INT_MAX;
self.view.backgroundColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:red green:green blue:blue alpha:1.0];
//perform animation (anything you like)使用 UIView 动画更简单
[UIView animateWithDuration:1.0 animations:^{
//scale, rotate and fade the view
CGAffineTransform transform = CGAffineTransformMakeScale(0.01, 0.01);
transform = CGAffineTransformRotate(transform, M_PI_2);
coverView.transform = transform;
coverView.alpha = 0.0;
} completion:^(BOOL finished) {
//remove the cover view now we're finished with it
[coverView removeFromSuperview];
}];
}
在动画过程中取消动画
可以用-addAnimation:forKey:方法中的key参数来在添加动画之后检索一个动画,使用如下方法:- (CAAnimation *)animationForKey:(NSString *)key;。但并不支持在动画运行过程中修改动画,所以这个方法主要用来检测动画的属性,或者判断它是否被添加到当前图层中。
为了终止一个指定的动画,你可以用如下方法把它从图层移除掉:-(void)removeAnimationForKey:(NSString *)key;或者移除所有动画:- (void)removeAllAnimations;。
图层时间
CAMediaTiming协议
CAMediaTiming协议定义了在一段动画内用来控制逝去时间的属性的集合,CALayer和CAAnimation都实现了这个协议,所以时间可以被任意基于一个图层或者一段动画的类控制。
持续和重复
duration是一个CFTimeInterval的类型(类似于NSTimeInterval的一种双精度浮点类型),对将要进行的动画的一次迭代指定了时间。
repeatCount,代表动画重复的迭代次数。
duration和repeatCount默认都是0。但这不意味着动画时长为0秒,或者0次,这里的0仅仅代表了“默认”,也就是0.25秒和1次。
相对时间
每次讨论到Core Animation,时间都是相对的,每个动画都有它自己描述的时间,可以独立地加速,延时或者偏移。
beginTime指定了动画开始之前的的延迟时间。这里的延迟从动画添加到可见图层的那一刻开始测量,默认是0(就是说动画会立刻执行)。
speed是一个时间的倍数,默认1.0,减少它会减慢图层/动画的时间,增加它会加快速度。如果2.0的速度,那么对于一个duration为t的动画,实际上在0.5t秒的时候就已经完成了。
timeOffset和beginTime类似,增加timeOffset只是让动画快进到某一点,例如,对于一个持续t秒的动画来说,设置timeOffset为0.5意味着动画将从一半的地方开始。
和beginTime不同的是,timeOffset并不受speed的影响。所以如果你把speed设为2.0,把timeOffset设置为0.5,那么你的动画将从动画最后结束的地方开始,因为t秒的动画实际上被缩短到了0.5t秒。然而即使使用了timeOffset让动画从结束的地方开始,它仍然播放了一个完整的时长,这个动画仅仅是循环了一圈,然后从头开始播放。
fillMode
对于beginTime非0的一段动画来说,会出现一个当动画添加到图层上但什么也没发生的状态。类似的,removeOnCompletion被设置为NO的动画将会在动画结束的时候仍然保持之前的状态。这就产生了一个问题,当动画开始之前和动画结束之后,被设置动画的属性将会是什么值呢?
这种行为就交给开发者了,它可以被CAMediaTiming的fillMode来控制。fillMode是一个NSString类型,可以接受如下四种常量:kCAFillModeForwards、kCAFillModeBackwards、kCAFillModeBoth、kCAFillModeRemoved。
默认是kCAFillModeRemoved,当动画不再播放的时候就显示图层模型指定的值。剩下的三种类型向前,向后或者即向前又向后去填充动画状态,使得动画在开始前或者结束后仍然保持开始和结束那一刻的值。
层级关系时间
每个图层是如何相对在图层树中的父图层定义它的坐标系的。动画时间和它类似,每个动画和图层在时间上都有它自己的层级概念,相对于它的父亲来测量。对图层调整时间将会影响到它本身和子图层的动画,但不会影响到父图层。
对CALayer或者CAGroupAnimation调整duration和repeatCount/repeatDuration属性并不会影响到子动画。但是beginTime,timeOffset和speed属性将会影响到子动画。然而在层级关系中,beginTime指定了父图层开始动画(或者组合关系中的父动画)和对象将要开始自己动画之间的偏移。类似的,调整CALayer和CAGroupAnimation的speed属性将会对动画以及子动画速度应用一个缩放的因子。
全局时间和本地时间
CoreAnimation有一个全局时间的概念,也就是所谓的马赫时间。马赫时间在设备上所有进程都是全局的–但是在不同设备上并不是全局的。可以使用CACurrentMediaTime函数来访问马赫时间:CFTimeInterval time = CACurrentMediaTime();,它返回了设备自从上次启动后的秒数,它真实的作用在于对动画的时间测量提供了一个相对值。注意当设备休眠的时候马赫时间会暂停,也就是所有的CAAnimations(基于马赫时间)同样也会暂停。
每个CALayer和CAAnimation实例都有自己本地时间的概念,是根据父图层/动画层级关系中的beginTime,timeOffset和speed属性计算。就和转换不同图层之间坐标关系一样,CALayer同样也提供了方法来转换不同图层之间的本地时间。如下:
- (CFTimeInterval)convertTime:(CFTimeInterval)t fromLayer:(CALayer *)l;
- (CFTimeInterval)convertTime:(CFTimeInterval)t toLayer:(CALayer *)l;
当用来同步不同图层之间有不同的speed,timeOffset和beginTime的动画,这些方法会很有用。
暂停,倒回和快进
设置动画的speed属性为0可以暂停动画,但在动画被添加到图层之后不太可能再修改它了,所以不能对正在进行的动画使用这个属性。
如果把图层的speed设置成0,它会暂停任何添加到图层上的动画。类似的,设置speed大于1.0将会快进,设置成一个负值将会倒回动画。
一个简单的方法是可以利用CAMediaTiming来暂停图层本身。通过增加主窗口图层的speed,可以暂停整个应用程序的动画。这对UI自动化提供了好处,我们可以加速所有的视图动画来进行自动化测试(注意对于在主窗口之外的视图并不会被影响,比如UIAlertview)。可以在app delegate设置如下进行验证:self.window.layer.speed = 100;